Australia, being a vast country, experiences multiple time zones, which can cause some confusion for travelers and residents alike.
This article breaks down the intricacies of Australian time, covering its various time zones, daylight saving adjustments, and how they impact both the local population and international interactions.
Whether you are in Sydney, Perth, or anywhere in between, knowing the local time is crucial for everything from business dealings to coordinating travel.
Time Zones Across Australia
Australia is divided into three primary time zones:
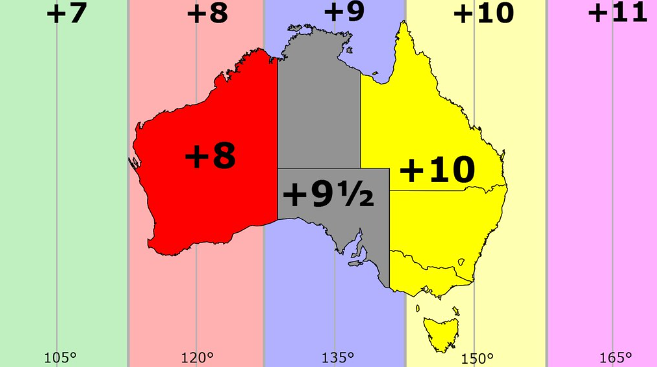
Australian Western Standard Time (AWST): UTC+8
Australian Central Standard Time (ACST): UTC+9:30
Australian Eastern Standard Time (AEST): UTC+10
Each time zone applies to different states and territories across the country:
AWST is used in Western Australia, with major cities like Perth following this zone.
ACST is followed by South Australia, the Northern Territory, and the town of Broken Hill in New South Wales.
AEST applies to states like New South Wales, Victoria, Tasmania, and Queensland. Notably, major cities like Sydney, Melbourne, and Brisbane fall within this time zone.
Time Zone Map
The time zones in Australia are not uniformly distributed across the country. The eastern states (like New South Wales and Victoria) follow AEST, while the central regions follow ACST. Western Australia, being isolated by distance, operates on AWST.
Understanding this geography is crucial for both domestic and international interactions, especially when scheduling meetings or travel plans.
Daylight Saving Time (DST)
Australia observes Daylight Saving Time (DST) in certain states during the warmer months, typically from October to April. However, not all regions participate. The following states and territories observe DST:
New South Wales
Victoria
South Australia
Tasmania
Australian Capital Territory
These states shift their clocks forward by one hour during DST, meaning the time zones change as follows:
Australian Eastern Daylight Time (AEDT): UTC+11
Australian Central Daylight Time (ACDT): UTC+10:30
Notably, Queensland, Western Australia, and the Northern Territory do not observe DST, remaining on their standard times throughout the year.
Why Some States Don’t Observe DST
The decision not to observe daylight saving is mainly due to climatic differences across Australia. States like Queensland and Western Australia, which are closer to the equator, have more consistent daylight hours throughout the year. For them, DST would bring little benefit, and in some cases, it can even cause disruptions to daily life.
Time Differences Between Australian Cities
Given the variations in time zones and the application of daylight saving, the time difference between major Australian cities can vary. For example:
Sydney (AEDT) can be three hours ahead of Perth (AWST) during daylight saving.
Adelaide (ACDT) is often half an hour behind Sydney but remains ahead of Perth by 2.5 hours during the same period.
During non-daylight saving months, the time difference between Sydney and Perth narrows to two hours, while Adelaide remains half an hour behind Sydney and 1.5 hours ahead of Perth.
Australia’s Global Time Comparisons
For international travelers or businesses, comparing Australian time zones to other countries is critical. Here are some notable comparisons:
Australia vs. the UK: During the UK’s standard time (UTC+0), Australia is significantly ahead. Sydney is typically 10 hours ahead of the UK (or 11 hours during AEDT).
Australia vs. the US: The time difference varies widely depending on which part of the US you’re comparing to. For instance, Sydney is 14 to 16 hours ahead of New York, depending on DST in both countries.
These significant differences can make scheduling meetings or flights between Australia and other countries challenging, so planning in advance is essential.
Importance of Time in Daily Life
The diverse time zones and the use of daylight saving time impact Australians in various ways:
Business and Commerce
Australia’s time zones, combined with its large geographic spread, play a critical role in the country’s commerce. For instance, when businesses in Perth start their day at 9 AM, it’s already 12 PM in Sydney, creating a significant lag for companies that operate across states.
This time difference can also complicate international trade, particularly with Europe and the Americas, where the time difference ranges from 10 to 18 hours, depending on the location.
Sports and Entertainment
Australians often have to adjust their schedules to watch live sports events or participate in global entertainment phenomena.
For example, major international sports events like the Olympics or the FIFA World Cup are often broadcast in the middle of the night due to time zone differences, meaning Australians must stay up late or wake up early to catch these events live.
Travel Across Australia
For travelers within Australia, adjusting to time differences is essential. A flight from Perth to Sydney crosses two time zones and can take up to five hours. Additionally, the arrival time in Sydney will be several hours ahead of the departure time from Perth, adding an extra layer of complexity to travel itineraries.
The Future of Time Zones in Australia
There have been discussions about whether Australia should adjust its time zones or even abolish daylight saving time altogether.
Some business groups and politicians have argued that simplifying the country’s time zones could make it easier to coordinate across states and territories, as well as improve international business dealings. However, no major changes have been proposed yet, and the current system remains in place.
FAQs
Q: What is the time difference between India and Australia?
A: The time difference between India and Australia depends on the specific timezone in Australia. It ranges from 2.5 hours ahead (AEST) to 3.5 hours behind (AWST) Indian Standard Time (IST).
Q: Does Australia observe daylight saving time?
A: Yes, most of Australia observes daylight saving time during the summer months. The specific dates for daylight saving time vary between states.
Q: How can I find the current time in Australia?
A: You can easily find the current time in Australia using online time zone converters or by checking your device’s settings.
Q: What is the best time to call Australia from India?
A: The best time to call Australia from India depends on the specific timezone you want to reach. Generally, early morning or late evening in India would correspond to suitable daytime hours in Australia.
Q: Are there any significant time zone differences within Australia?
A: Yes, there are significant time zone differences within Australia. This can be important to consider when planning travel or scheduling calls.
Conclusion
Understanding the time zones across Australia is crucial for residents and international visitors alike. Whether you’re navigating the local differences between Sydney and Perth, or trying to coordinate a meeting with someone overseas, Australia’s unique time system can pose both challenges and opportunities.
Keeping track of daylight saving time and the differences between cities will help ensure that you’re always on time, no matter where you are in the country.
Australia’s time system may seem complex at first glance, but once understood, it provides a fascinating glimpse into how a vast nation manages its hours across diverse regions and climates.
To read more, click here.